Osteoarthritis is considered one of the most common joint diseases. According to the Deutsche Arthrose-Hilfe e. V. (German Osteoarthritis Association), around five million people in Germany suffer from symptoms caused by the destruction of the cartilage layer of a joint and the associated bone changes. Two million men and women even experience pain in their joints on a daily basis. Arthritis, an inflammatory joint disease that can occur in episodes, must be distinguished from osteoarthritis. According to the German Society for Rheumatology (Deutsche Gesellschaft für Rheumatologie e. V.), there are approximately 560,000 – 830,000 people affected in Germany. What you need to know about the difference between osteoarthritis and arthritis, as well as the treatment, you will learn below.

The difference between osteoarthritis and arthritis
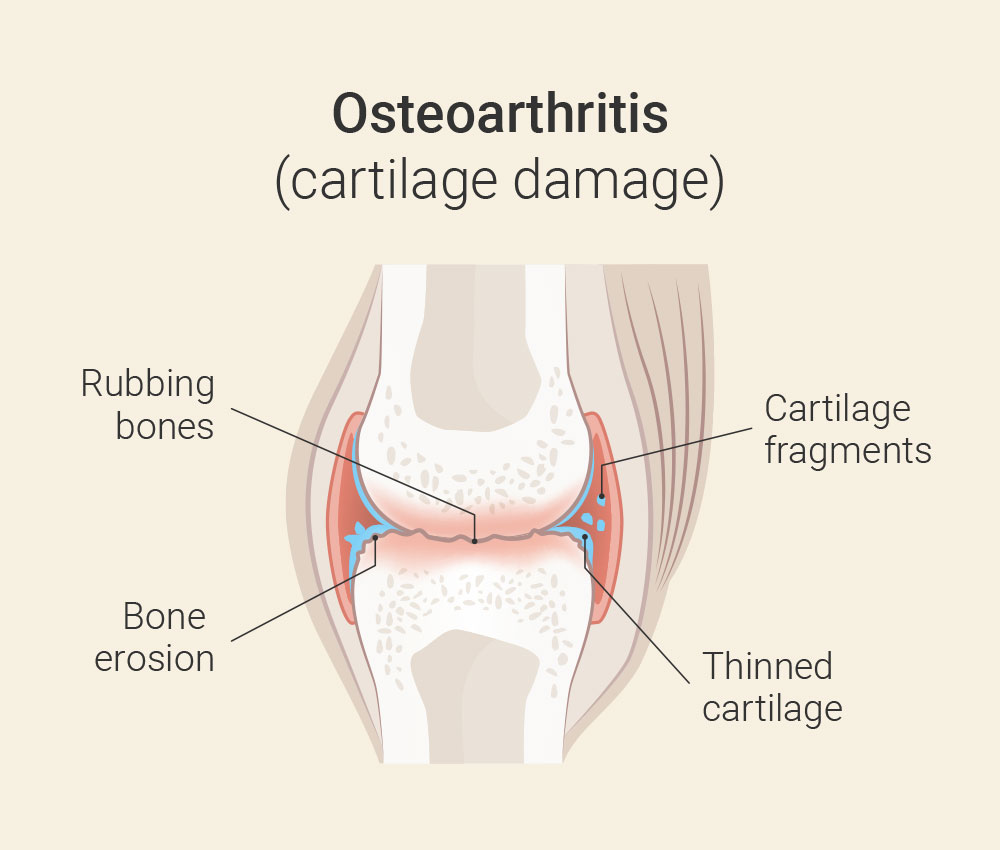
Profile Osteoarthritis: When joint cartilage is irreparably damaged
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease in which the cartilage in one or more joints is worn away and damaged. Cartilage normally has the job of protecting joints and allowing them to move smoothly. However, in osteoarthritis, it gradually becomes thinner. It may even wear away completely, causing the bones to rub directly against each other. The worn cartilage and bone surfaces can be painful and cause inflammation in the joint. This can lead to symptoms such as pain, stiffness, swelling and limited mobility. Osteoarthritis often occurs in joints such as the hands, knees, hips and spine, but in principle can affect any joint.
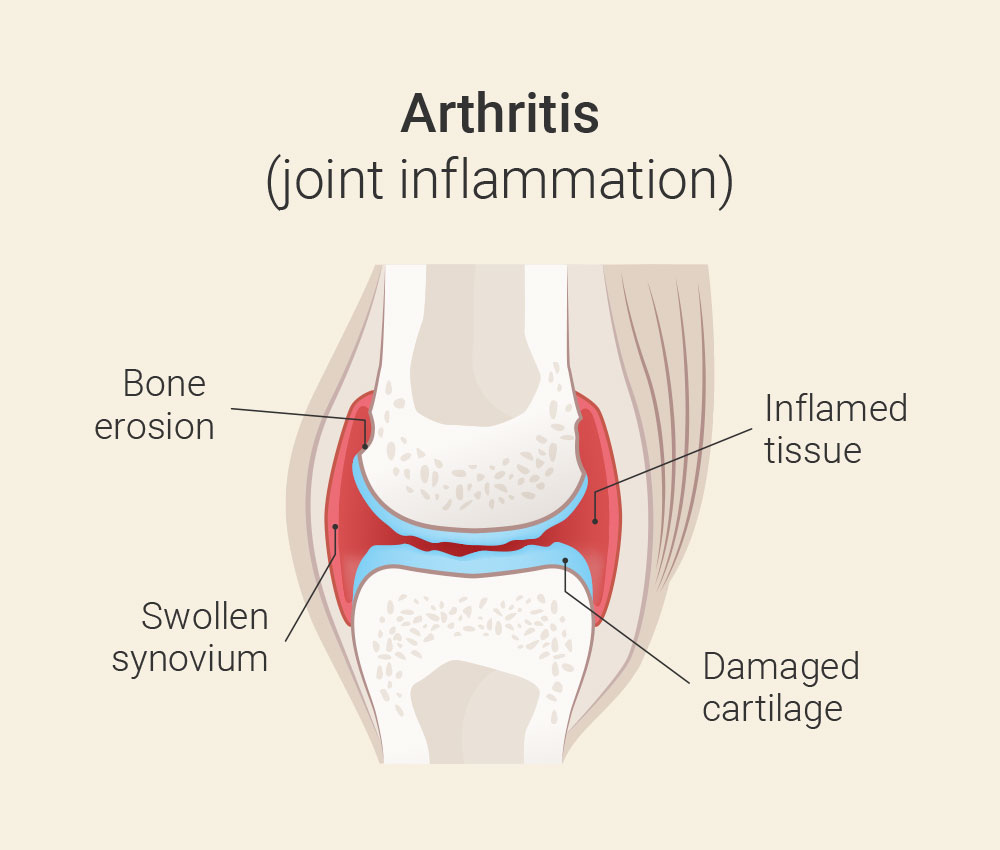
Profile Arthritis: Inflammatory joint disease
Arthritis is an inflammatory disease of the joints that causes swelling, pain and limited mobility. There are several forms of arthritis, the most common being rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in the joints. This leads to inflammation and damage to the joint cartilage and surrounding tissue. Rheumatoid arthritis usually affects several joints at once and can also damage other organs and tissues in the body. Osteoarthritis, also known as degenerative joint disease or “wear and tear” arthritis, occurs when the cartilage in the joints gradually breaks down. Aging, long-term overuse of joints, injury, congenital joint defects, infection, gout or metabolic disorders can cause osteoarthritis.
Osteoarthritis therapy in our practice in Frankfurt
Treatment for osteoarthritis generally aims to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, improve joint function and prevent progression of the disease. Specific treatment methods may vary depending on the severity of the osteoarthritis and the joints affected.
At our private practice for orthopedics and traumatology in Frankfurt, we offer careful examination and consultation as well as:
Peri- and intra-articular infiltrations.
In this procedure, we inject anti-inflammatory substances into the affected joint or the surrounding soft tissues. In this way, we can improve the effects of painful overuse or incorrect strain syndromes as well as signs of wear and tear.
Autologous blood therapy
For this purpose, we use your own blood and prepare it so that we can inject the platelet-rich plasma it contains into the inflamed areas. You can also learn more about the mode of action here: “PRP therapy for osteoarthritis“
Kinesio-Taping
We apply special tapes to your muscles or tissues, which have a relaxing and stabilizing effect on the joint structures.
Acupuncture
This procedure is based on Traditional Chinese Medicine. By inserting fine needles into your tissue, we create a mild and harmless inflammatory stimulus that stimulates your body. This can cause improved blood flow to the affected area, while also having anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving effects.
Conservative treatment, aids, physiotherapy & co.
We can also use painkillers such as acetaminophen or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to relieve pain. For more severe pain, we can also prescribe stronger painkillers. Bandages and orthotics, as well as physical therapy, have continued to prove effective.
Arthritis therapy in our practice in Frankfurt
In the case of joint inflammation, there are various ways to relieve acute discomfort. Anti-inflammatory drugs and painkillers can provide short-term relief. However, long-term measures also play an important role in treatment. Careful mobilization of the affected joints can help you reduce symptoms and improve mobility. Physical therapy and occupational therapy offer specific exercises and techniques to strengthen joint function and relieve pain.
Dietary changes can also have positive effects. A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory nutrients such as omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants and fiber can help reduce inflammation in the body. Depending on the exact diagnosis, the use of specific medications may also be useful. In the case of rheumatoid arthritis, we may also work with a rheumatologist.
Image sources: 518233562 © Oporty786 | 144114782 © elenabsl | stock.adobe.com